[ad_1]
As enterprises increasingly migrate their workloads to cloud infrastructure, the need for robust security measures becomes more pressing.
Unlike traditional data centers, cloud environments offer business agility at a reduced cost, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals.
Defending cloud infrastructure, particularly within Amazon Web Services (AWS), is complex and requires a nuanced understanding of security controls and threat detection.
This article explores how defenders can address detection gaps in AWS environments by leveraging a combination of Mitigant Cloud Attack Emulation and the Sekoia Security Operations Center (SOC) Platform.
The integration of these tools demonstrates a Threat-Informed Defense strategy that enhances an organization’s ability to detect and respond to threats effectively.
Enterprises are increasingly adopting cloud infrastructure to benefit from its agility and cost-effectiveness. However, this shift has not gone unnoticed by cybercriminals, who now target cloud workloads with sophisticated attacks.
Defending cloud environments is inherently more complex than on-premises infrastructure, necessitating a comprehensive approach to security.
The Sekoia report provides a use-case scenario demonstrating how defenders can address detection gaps in AWS environments by combining Mitigant Cloud Attack Emulation and the Sekoia SOC Platform.
It also discusses how organizations can adopt a Threat-Informed Defense strategy by integrating security measures, Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI), and evaluation/testing.
This strategy enables organizations to detect and respond effectively to threats within their AWS infrastructure.
Threat Model
The threat model features Acme, a fictitious Fintech company hosting its banking system on AWS cloud infrastructure. John Doe, Acme’s Chief Information Security Officer (CISO), is concerned about the increasing threat Scattered Spider poses.
After attending an MITRE ATT&CK Workshop, John decides to implement a Threat-Informed Defense Strategy (TIDS) to enhance Acme’s cyber-resilience.
He incorporates the following cybersecurity products to align with TIDS:
- Defensive Measures: Sekoia Defend is a leading SOC platform that provides threat detection and incident response capabilities.
- Cyber Threat Intelligence: Sekoia Intelligence, a structured and actionable CTI service.
- Testing & Evaluation: Mitigant Cloud Attack Emulation, a comprehensive cloud-native adversary emulation platform.
The Threat-Informed Defense Triad combines security measures, CTI, and security evaluation/testing to create a robust defense strategy.
Mitigant Cloud Attack Emulation implements several MITRE ATT&CK Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs) Scattered Spider uses.
Join our free webinar to learn about combating slow DDoS attacks, a major threat today.
These attacks are orchestrated against Acme’s AWS environment to mimic Scattered Spider, and the Sekoia SOC Platform is used to detect these attacks.
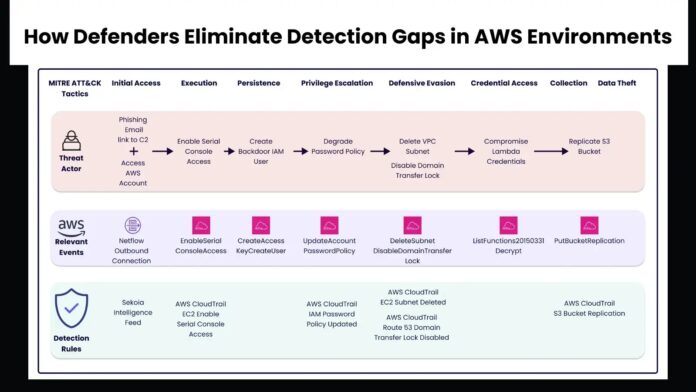
Cloud Attack Phases and Detection
The threat scenario is emulated to illustrate real attacks, which are typically multi-step and captured via attack kill chains. The MITRE ATT&CK framework groups these attacks into Tactics and Techniques. The attacks against Acme are categorized as follows:
Initial Access
The attacker gains access to Acme’s corporate AWS account using stolen credentials obtained through phishing. Bob from Acme’s finance department receives a malicious email containing a link to a fake corporate website.
The user’s workstation logs this activity, and Sekoia.io’s Intelligence Feed rule detects suspicious IP access.

Execution
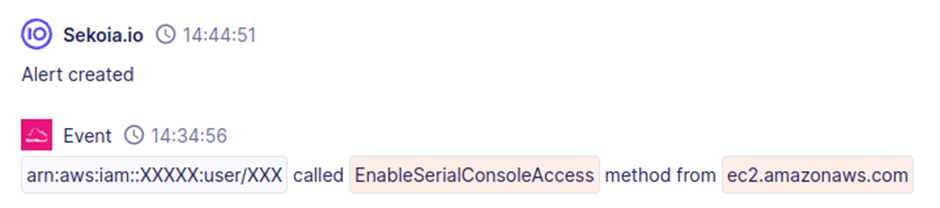
The attacker enables serial console access to EC2 instances, bypassing network security controls. This action is detected by the Sekoia.io rule “AWS CloudTrail EC2 Enable Serial Console Access.”
Persistence
The attacker creates new IAM users and backdoors existing IAM users, raising the “CreateAccessKey” and “CreateUser” events. Specific detection rules tailored to the environment can help identify these activities.
Privilege Escalation
The attacker weakens IAM password policies to facilitate further attacks, triggering the “UpdateAccountPasswordPolicy” event. The Sekoia.io rule “AWS CloudTrail IAM Password Policy Updated” monitors this event.

Defense Evasion
The attacker deletes VPC subnets and disables domain transfer locks to hide their activities. These actions are detected by the Sekoia.io rules “AWS CloudTrail EC2 Subnet Deleted” and “AWS CloudTrail Route 53 Domain Transfer Lock Disabled.”

Credential Access
The attacker compromises Lambda credentials, raising the “ListFunctions20150331” event. Due to their frequency, creating effective detection rules for these events can be challenging.

Collection
The attacker replicates S3 buckets and exfiltrates sensitive data, triggering the “PutBucketReplication” event. The Sekoia.io rule “AWS CloudTrail S3 Bucket Replication” detects this action.

The integration of CTI helps detect and contextualize attacks, providing a better understanding for further investigation. Alert fatigue is a significant challenge for SOC teams, and triaging rules by effort level can help manage this issue.
Sometimes, customers should create their own rules to reduce false positives. Attack emulation is essential for testing rules and ensuring comprehensive coverage. Context is crucial, and security teams must add context to reduce false positives.
Emulating attacks in the environment provides an excellent approach for deriving the precise context. As cloud infrastructure adoption increases, so do the associated security risks.
Security teams must adopt approaches that allow precise threat optimizations with minimal alert fatigue and false positives. A Threat-Informed Defense strategy provides a meaningful approach, aligning with real attacks.
This article presents an instructive scenario based on the Scattered Spider threat actor, offering valuable lessons for improving cloud security posture.
By adopting a Threat-Informed Defense strategy and leveraging tools like Mitigant Cloud Attack Emulation and the Sekoia SOC Platform, organizations can effectively eliminate detection gaps in AWS environments and safeguard their cloud infrastructure against sophisticated cyber threats.
Protect Your Business Emails From Spoofing, Phishing & BEC with AI-Powered Security | Free Demo
[ad_2]
Source link