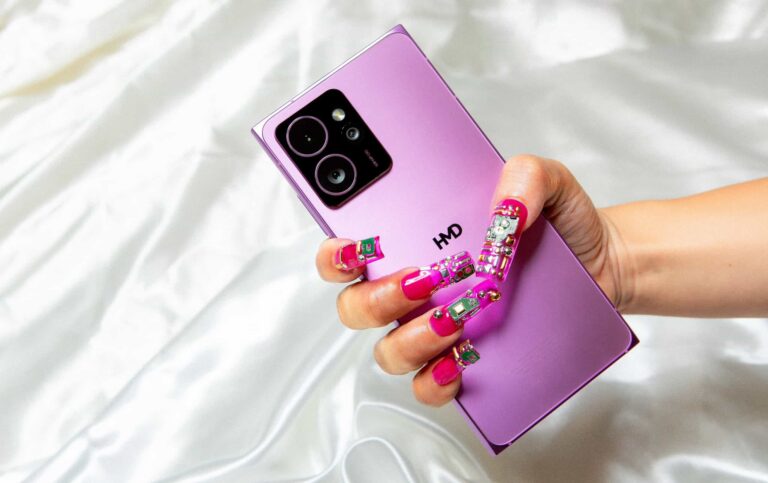
Human Mobile Devices, popularly known as HMD and the maker of Nokia phones, has launched a new mid-range Android phone. The HMD Skyline resembles Samsung’s Galaxy S24 Ultra thanks to its sharp corners but isn’t as powerful. However, it has some specialties. First, the device has a user-removable back plate for enhanced repairability. It is also the world’s first Android phone to support Qi2 wireless charging.
HMD Skyline launched with a 108MP camera and Qi2 wireless charging
Powered by Qualcomm’s Snapdragon 7s Gen 2, the HMD Skyline packs some amazing specs for a mid-range phone. It sports a 6.55-inch Full HD+ OLED display (1080×2400 pixels resolution) with 1,000 nits of brightness, a 144Hz refresh rate, and Corning Gorilla Glass 3. The phone is available in 8GB and 12GB RAM variants with 128GB and 256GB storage options. It supports 1TB microSD cards.
Cameras are one of the HMD Skyline’s strengths. Its 108MP primary rear camera boasts OIS (Optical Image Stabilization) and supports 4K video recording with spatial audio capture and wind noise reduction. The phone also has a 13MP ultrawide lens and a 50MP telephoto camera with up to 4x optical zoom. You don’t often see a zoom camera on a mid-range phone. There’s a 50MP selfie camera on the front.
This 5G-ready HMD phone boasts Wi-Fi 6E, Bluetooth v5.2, NFC, and GPS connectivity options. It is fueled by a 4,600mAh battery with 33W wired charging, 15W Qi2 wireless charging, and 5W reverse wireless charging. The latter two technologies are a rarity in this segment. Other highlights include a side-mounted fingerprint scanner, a programmable custom button, an IP54 rating, and Android 14.
With a thickness of 8.9mm, the HMD Skyline is quite bulky, particularly when you consider the battery capacity. It appears this is a compromise we must make for a removable back plate. A screw holds the back cover, so you don’t need a heat gun, pry tool, and other equipment to remove it. If you aren’t comfortable opening it up yourself, HMD has partnered with iFixit for easy repairability of the phone.
Price and availability
HMD’s Skyline comes in Neon Pink and Twisted Black colors. It is currently available in the UK at £399.99 for the 8GB+128GB model and £499.99 for the 12GB/256GB model. The phone will also come to the US but the company hasn’t revealed prices yet. Replacement parts and repair kits are available from iFixit for the display, back cover, sub-board/charging port, and battery. It’s unclear if HMD plans to release this phone outside of the US and Europe.
[ad_2]
Source link






.webp)
.webp)
.webp)





.webp)
.webp)
.webp)